Brain Tumors
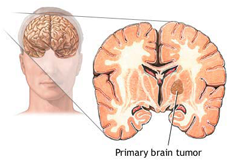
Primary brain tumors can start from brain cells, the membranes around the brain (meninges), nerves, or glands. Tumors destroy brain cells directly. They can also damage cells by producing inflammation, placing pressure on other parts of the brain, and increasing pressure within the skull.The cause of primary brain tumors is unknown. However they are created by an abnormal and uncontrolled cell division, usually in the brain itself. Brain tumors are classified depending on the location of the tumor, the type of tissue involved and whether they are noncancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant)
The symptoms of brain tumors depend on their size and location in the brain. Symptoms often are caused by damage to vital tissue and pressure on the brain as the tumor grows within the limited space in the skull. If a brain tumor grows very slowly, its symptoms may not appear for some time. The most frequent symptoms of brain tumors include Headaches (worse in the morning and ease during the day), Nausea or vomiting, Seizures, Weakness or loss of feeling in the arms or legs, Lack of coordination, Abnormal eye movements, Drowsiness, Changes in personality or memory, Changes in speech
Treatment
Treatment can involve surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Early treatment often improves the chance of a good result. However the treatment method depends on the size and type of tumor and your general health. Surgery is often needed for most primary brain tumors. Some tumors may be completely removed. Those that are deep inside or enter brain tissue may be debulked instead of removed.
Other medications used to treat primary brain tumors include:
- Corticosteroids to reduce brain swelling
- Mannitol to reduce brain swelling and pressure
- Anticonvulsants to reduce seizures
- Pain medications
- Antacids or histamine blockers to control stress ulcers
 Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's Disease